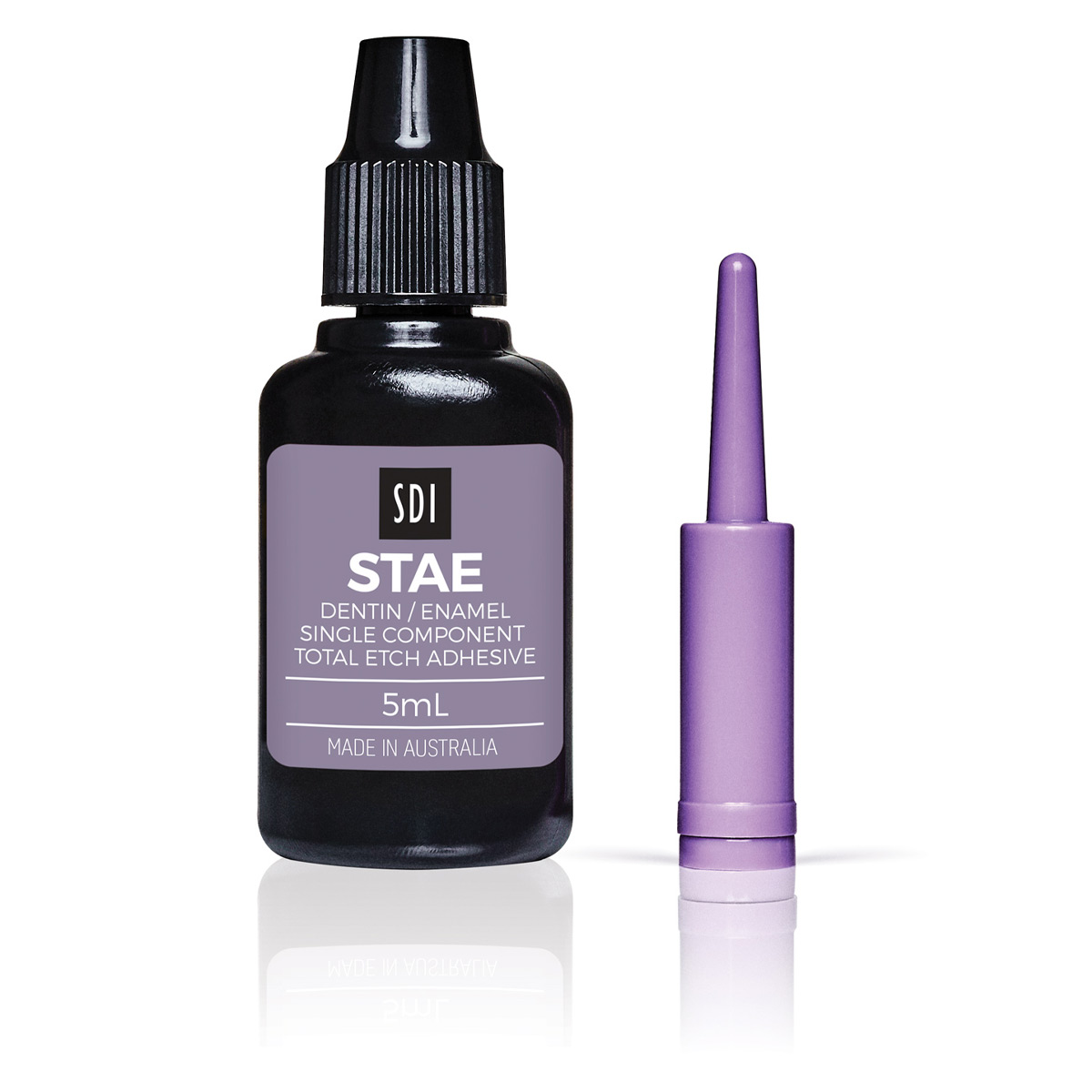
Fluoride release
Fluoride’s cariostatic effect enhances remineralization and inhibits enamel demineralization. In an aqueous environment, the fluoride ions in Stae diffuse from the resin into the surrounding tooth. This ionic movement is caused by oral fluid passing in and out of the resin and tooth, acting as a carrier for the fluoride ions.
Bonds to moist and dry tooth surfaces
Stae’s carrier solvent is a mixture of acetone and water. The acetone carries Stae deep into the demineralized dentin and the water re-moistens any dry dentin.
Dental Advisor rating
“Stae is a highly recommended adhesive system designed for composite, compomer, and porcelain bonding. It received an 86% rating.”(1)